Last updated: July 2023
Also known as…Hormonal acne, female acne, post-adolescent acne, late onset acne.
What is adult acne?
Adult acne is acne that continues past the teenage years into adulthood or starts in adulthood in those who may not have had a previous problem with acne during teenage years.
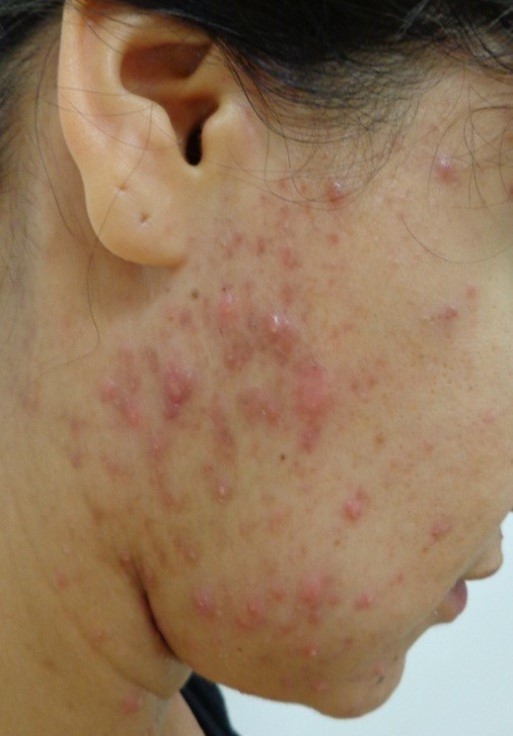
Figure 1. Hormonal acne. Image reproduced with permission of Dr Jo-Ann See
Who gets adult acne?
Adult acne is more frequently seen in women. It is usually less common in men.
What causes adult acne?
Several factors may cause adult acne, including:
- Increased oiliness (sebum production)
- Increased acne bacteria in the oil glands
- Cell build-up (abnormal keratinisation) within the oil gland
- Inflammation
It is unclear whether increased levels of male hormones (androgens) in the blood or small amounts of locally produced male hormones stimulate oil glands to produce more oil or sebum.
Laboratory investigations are often normal in these patients. A dermatologist may look for evidence of increased hair growth, female patterned scalp hair loss and irregular menstruation. Other clinical features could be problems with infertility or signs of insulin resistance.
Some medications may precipitate or aggravate acne.
What does adult acne look like?
Adult acne usually looks like adolescent or teenage acne vulgaris. It often presents with whiteheads, blackheads, red bumps (papules), pimples and inflamed pus-filled spots (pustules, nodules, cysts), which can lead to scarring.
Adult acne often occurs on the face around the lower cheeks, jawline and neck. In some cases, adult acne can develop on the back and chest.
Increased oiliness may be noticed on the scalp. The post- inflammatory healing phase with redness or brown hyperpigmentation is also seen.
The acne lesions are often tender and long lasting.
Many women affected with adult acne experience a flare-up of their acne the week prior to their menstrual cycle.
How is adult acne diagnosed?
Adult acne is diagnosed clinically by observing the presence of whiteheads, blackheads, red pumps, and pimples and inflamed pus-filled spots on the face, chest or back.
In some cases, further blood or imaging investigations may be needed if there are suspected hormonal abnormalities or signs of insulin resistance.
How is adult acne treated?
Treatment options will vary depending on the individual and their needs.
Adult acne treatment is the same as for acne vulgaris, and may include:
- Combination therapy with topical and oral agents
- Hormonal treatments with oral contraceptive
- Hormonal blocking agents, such as spironolactone or cyproterone acetate
In adult acne cases that are resistant to treatment, long-term low dose oral isotretinoin may be prescribed by dermatologists.
What is the likely outcome of adult acne?
Adult acne is often characterised by flare-ups and acne-free periods. This may continue for several years but can usually be suppressed with treatment.
Adult acne can be persistent for many years into a person’s 30s and 40s. In severe acne, scarring can develop because of deeper, more severe inflammation or pus-filled spots.
| Dr JoAnn See | July 2023 |
| Dr JoAnn See | October 2015 |
Disclaimer
2019 © Australasian College of Dermatologists.
You may use for personal use only. Please refer to our disclaimer.