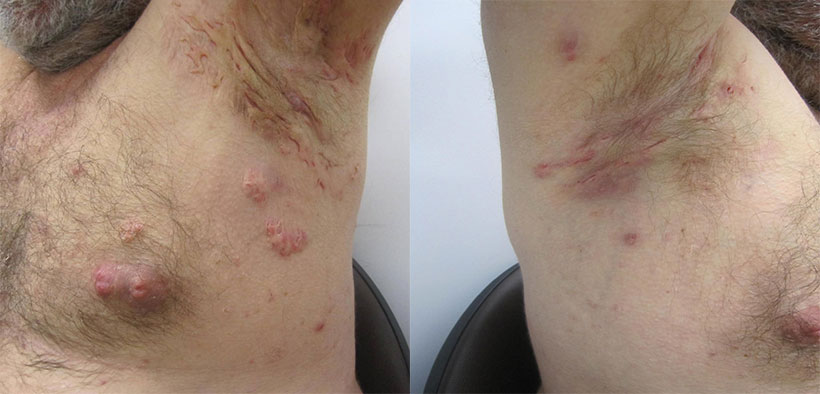
Hidradenitis suppurativa is a condition affecting apocrine sweat glands that are located mostly under the arms and in the groin and genital area. These glands become blocked and cause an exaggerated inflammatory response. The resulting inflamed cysts are painful and often recur. The painful and recurrent nature of this disease can be very distressing to the affected individuals and impacts greatly on their quality of life.
The cause of hidradenitis suppurativa is unknown. It is thought that there is an exaggerated inflammatory response to the presence of bacteria trapped in obstructed hair follicles in the skin. In some cases there does seem to be a genetic component. Bacteria seem to play some role which is why antibiotics may be used in treatment. However, bacteria are not the primary cause of the condition. Other factors such as obesity, smoking and stress also play a role.
Hidradenitis suppurativa usually starts with blockage of the apocrine or sweat glands. These blockages form comedones or blackheads. Inflammation can then develop, leading to redness and swelling. Advanced disease can lead to severe and disfiguring scarring.

Pain associated with this condition can be severe and interfere with everyday activities. Secondary infections can occur which may be serious. The scarring can cause narrowing of the anus, rectum or urethra and lead to difficulty in passing stool or urine.
The diagnosis is usually made by a dermatologist. Biopsies and other tests are not required in most cases.
The condition is very difficult to treat and there is no single treatment that has been shown to be effective for everyone.
Affected individuals need to be supervised by a dermatologist with treatment tailored to their needs.
Lifestyle modifications such as smoking, losing weight and reducing stress are recommended, but there is little research evidence of how effective these modifications are.
The main method of treating mild disease involves antibacterial washes and topical antibiotics, and acute flare-ups may be managed by intralesional corticosteroids and /or minor surgical procedures.
Treatments include antibiotics and antibiotic combinations even if there is no evidence of secondary infection. Anti-androgens in both men and women can be useful, either on their own or in combination with antibiotics. Anti-inflammatory agents including oral corticosteroids and immunosuppressive agents such as dapsone, azathioprine, cyclophosphamide and methotrexate can be useful.
Newer biological agents have been trialled, including infliximab and adalimumab. Adalimumab has recently received Therapeutic Good Association (TGA) approval for use in hidradenitis suppurativa; however, it is only available through compassionate access schemes. There are a number of other treatments that have been tried including retinoids (vitamin A-like drugs), photodynamic therapy and laser treatment. Laser hair removal may be of some benefit but this treatment can be very costly.
Very severe cases often require surgery. The surgery can be extensive and is ideally carried out by a plastic surgeon who is familiar and experienced with this condition.
The way hidradenitis suppurativa develops in individual people is not very well understood. The condition is not curable but is generally controllable with one or more of the above treatments. Not all cases progress to the most severe form of the disease.
Treatment and control of the inflammation is important to minimise the condition progressing and scarring.
Weight gain and smoking worsen the condition and should be avoided. Hidradenitis suppurativa is generally most active during teenage years and young adulthood. It often, but not always, improves as the person gets older.
Further information
Disclaimer
2019 © Australasian College of Dermatologists.
You may use for personal use only. Please refer to our disclaimer.